Environmental Impact of 2-Bromoethanol: What You Should Know
Discover the environmental impact of 2-Bromoethanol, its effects on ecosystems, and potential solutions for reducing harm.
The presence of chemicals in our environment poses numerous risks, both visible and hidden. One such compound, 2-Bromoethanol, has raised concerns due to its various industrial uses and potential environmental impact. This article will explore the multifaceted effects of 2-Bromoethanol on the environment, its risks to public health, and the steps needed to mitigate these concerns.
Introduction to 2-Bromoethanol
What is 2-Bromoethanol?
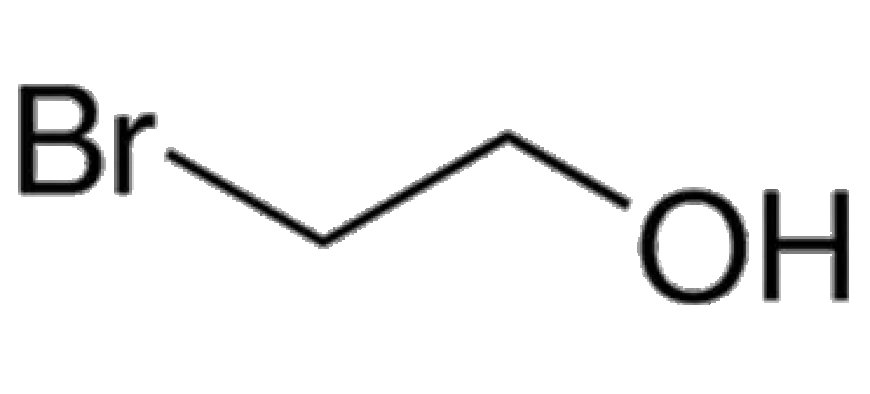
2-Bromoethanol, often abbreviated as BrCH2CH2OH, is an organic chemical compound used primarily in chemical synthesis. It is a bromo-substituted alcohol, frequently employed as a reagent in various chemical reactions, particularly in the production of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and organic compounds. The versatility of 2-Bromoethanol in industrial settings arises from its reactivity, making it useful in many applications.
While its chemical properties may be beneficial for industrial use, the environmental implications of 2-Bromoethanol raise questions about its safe handling and disposal. Its presence in ecosystems can lead to widespread contamination if not managed properly.
Common Applications of 2-Bromoethanol
2-Bromoethanol has diverse applications across multiple industries. It is often utilized in:
- Pharmaceutical production: As an intermediate in drug synthesis.
- Pesticide formulation: Serving as a precursor to more complex organic compounds.
- Laboratory settings: Employed as a reagent for organic synthesis and the preparation of other chemicals.
Despite its useful applications, its use has environmental consequences due to the way it can spread into natural systems, leading to contamination.
Environmental Impact of 2-Bromoethanol
Release and Distribution in the Environment
Once 2-Bromoethanol is released into the environment, either through improper disposal or accidental spills, it can enter air, water, and soil. Its behavior in the environment depends on various factors, including its chemical stability and interaction with environmental media. In the atmosphere, it may be subject to degradation, but in water and soil, it can persist for extended periods.
Persistence in Soil and Water
When 2-Bromoethanol enters water bodies, it may pose risks to aquatic life due to its toxicity and potential to bioaccumulate in organisms. In soil, the compound can leach into groundwater, creating further risks for both ecosystems and human populations. The persistence of 2-Bromoethanol in such environments underscores the importance of stringent regulatory measures to limit its spread.
Airborne Effects of 2-Bromoethanol
While less common, airborne exposure to 2-Bromoethanol can occur, especially in areas where it is produced or handled. Inhalation of the chemical can lead to respiratory issues in humans and animals alike. Industrial emissions, when not controlled, may release 2-Bromoethanol into the air, contributing to localized contamination.
Toxicity of 2-Bromoethanol
How 2-Bromoethanol Affects Aquatic Life
Aquatic ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to 2-Bromoethanol contamination. When the compound enters water bodies, it can affect the survival and reproduction of fish and other aquatic organisms. Its toxicity varies depending on the concentration, but even low levels can disrupt ecosystems by affecting the food chain. Furthermore, bioaccumulation can occur, where smaller organisms ingest the chemical and pass it up the food chain, amplifying its effects on larger species.
Terrestrial Impact: Soil and Plants
On land, 2-Bromoethanol can have detrimental effects on soil health. Once it enters the soil, it may inhibit plant growth, reducing crop yields and altering local ecosystems. Microbial populations in the soil, which are essential for nutrient cycling, can also be impacted, leading to long-term degradation of soil quality. This can, in turn, affect agricultural productivity and biodiversity.
Human Exposure and Health Risks
In addition to environmental effects, 2-Bromoethanol poses significant risks to human health. Direct exposure, either through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, can lead to a range of health issues. Short-term exposure may cause irritation of the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract, while long-term exposure can have more severe consequences, including neurological effects and potential carcinogenicity. As a result, safety protocols and protective measures are crucial in industries that use this chemical.
Mechanisms of Environmental Contamination
Industrial Emissions and Waste Disposal
Industries that manufacture or use 2-Bromoethanol must take care to prevent emissions and improper waste disposal. If not properly managed, waste products containing 2-Bromoethanol can seep into water sources or be released into the air, leading to widespread environmental contamination. Proper filtration, neutralization, and containment strategies are essential to reduce this risk.
Accidental Spills and Environmental Disasters
Accidental spills represent one of the most immediate threats to the environment when handling chemicals like 2-Bromoethanol. Such spills can quickly contaminate nearby ecosystems, especially if they occur near water bodies or within sensitive habitats. The rapid response is essential in such situations to prevent irreversible damage.
Bioaccumulation and Its Long-term Consequences
One of the most concerning aspects of 2-Bromoethanol is its potential to bioaccumulate. This process occurs when small amounts of the chemical accumulate in organisms over time, with higher concentrations occurring in species higher up the food chain. This can lead to long-term ecological disruption, as well as increased risks for predators, including humans, who may consume contaminated species. Chloromethyl methyl ether is a colorless liquid commonly used as a reagent in organic synthesis.
Addressing the Environmental Impact
Regulatory Measures and Environmental Standards
Governments and environmental agencies have established regulations for the safe handling, use, and disposal of 2-Bromoethanol. These measures are designed to minimize environmental contamination and protect public health. However, enforcement is crucial, and industries must comply with environmental standards to mitigate risks effectively.
Methods for Reducing Environmental Contamination
To reduce the environmental impact of 2-Bromoethanol, industries can adopt several strategies. These include:
- Improved waste treatment processes: Ensuring that chemical waste is neutralized before disposal.
- Use of advanced filtration technologies: To capture emissions before they are released into the environment.
- Routine environmental monitoring: To detect and address contamination early.
These steps not only help protect ecosystems but also safeguard human populations from exposure.
Safe Handling and Disposal Guidelines
Handling and disposing of 2-Bromoethanol require strict adherence to safety guidelines. Protective equipment, proper ventilation, and containment measures are vital in preventing exposure during handling. Additionally, disposal protocols should ensure that waste containing 2-Bromoethanol is treated and neutralized before being released into the environment, minimizing its ecological footprint.
Green Chemistry Alternatives
Safer Chemical Substitutes for 2-Bromoethanol
The search for safer alternatives to hazardous chemicals like 2-Bromoethanol is gaining momentum. Green chemistry principles encourage the development of chemicals that are less harmful to the environment and human health. By identifying and using alternative compounds with similar properties but reduced toxicity, industries can continue to meet their needs while reducing their environmental impact. With the growing demand for Tertiary Butyl Carbazate manufacturers in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, Indian manufacturers are expanding their production capacities.
Role of Biotechnology in Mitigating Harm
Biotechnology offers promising solutions for mitigating the environmental effects of chemicals like 2-Bromoethanol. Through bio-remediation, for example, microorganisms can be employed to break down toxic substances in the environment. Research in this area is ongoing, and advances could provide effective methods for reducing contamination in the future.
What's Your Reaction?


















