Tackle Melasma with Safe and Effective Methods
Discover safe and effective treatments for melasma, including topical treatments, chemical peels, lasers, and microneedling, for a more even skin tone.
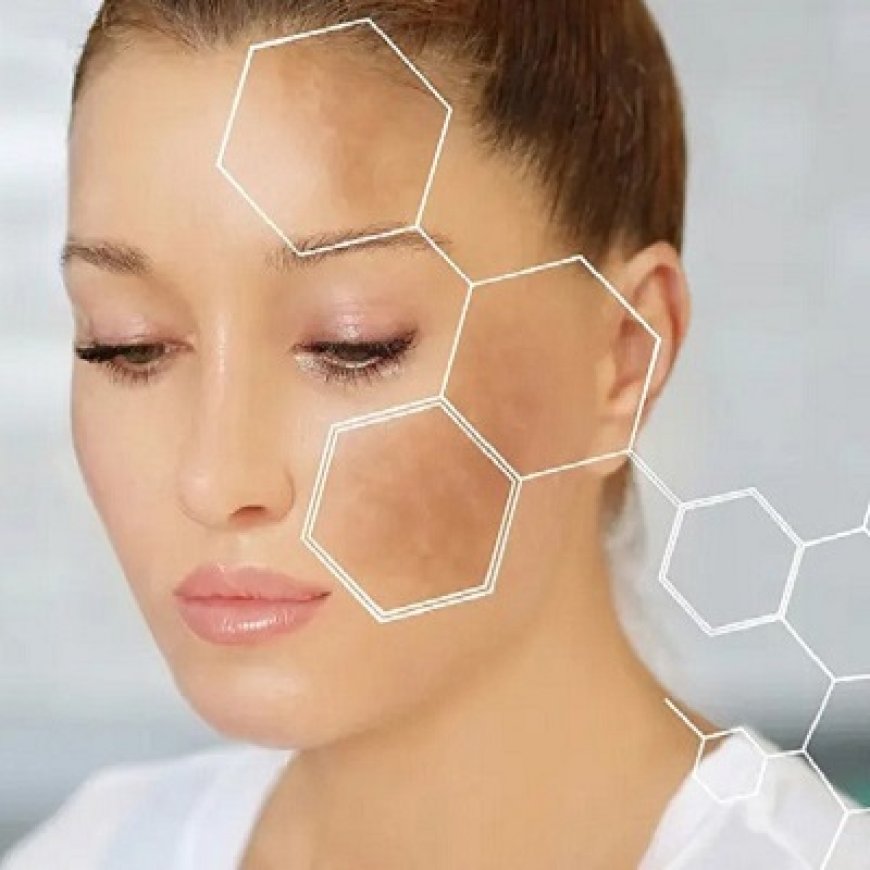

Melasma is a common skin condition that causes dark patches, usually on the face, due to an overproduction of melanin. Though harmless, it can affect your appearance and self-esteem. The good news is that melasma can be managed effectively with safe and proven treatments. In this blog, we’ll explore the best options to tackle melasma and achieve a more even skin tone.
What Causes Melasma?
Melasma in Islamabad occurs when the skin produces excess pigment, often as a response to triggers like sun exposure, hormonal changes, and genetics. Here are the primary causes:
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays can stimulate the production of melanin in the skin, leading to dark spots or patches.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy can trigger melasma, especially in women. It’s often called the "mask of pregnancy."
- Genetics: If your family has a history of melasma, you may be more prone to developing it.
- Skin Irritation: Certain cosmetic products can irritate the skin, exacerbating pigmentation issues.
Understanding these causes can help in preventing and treating melasma more effectively.
Safe and Effective Treatments for Melasma:
Luckily, there are several safe and effective methods to treat melasma. While each treatment varies based on skin type and severity of pigmentation, here are the most commonly used and proven options:
-
Topical Treatments:
Hydroquinone: This bleaching agent is one of the most effective treatments for melasma. It reduces melanin production and helps lighten dark patches.
Tretinoin: Also known as retinoid, tretinoin helps with cell turnover, which can prevent the buildup of pigmentation while improving overall skin texture.
Vitamin C: As a powerful antioxidant, Vitamin C helps to brighten skin and reduce hyperpigmentation caused by melasma. It also protects the skin from future sun damage.
Azelaic Acid: This ingredient inhibits melanin production and is known to be effective in treating melasma, especially for people with sensitive skin.
-
Chemical Peels:
Chemical peels are a non-invasive treatment that uses chemicals like alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or glycolic acid to exfoliate the skin. By removing the outermost layer of skin, chemical peels can lighten melasma spots and encourage the growth of healthier skin cells.
Glycolic acid peels and salicylic acid peels are especially effective for melasma, as they exfoliate and reduce hyperpigmentation over time.
-
Laser Treatments:
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) and Fractional CO2 lasers are commonly used to target melasma. These treatments work by breaking down the pigment in the skin without damaging surrounding tissue.
Lasers are particularly effective for stubborn melasma that doesn’t respond to topical treatments. However, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist to ensure you choose the right type of laser for your skin type.
-
Microneedling:
Microneedling involves the use of fine needles to create tiny channels in the skin, stimulating collagen production. This process can also help improve the absorption of brightening serums and treatments. When combined with Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), microneedling can boost skin regeneration and further reduce pigmentation.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP):
PRP therapy involves using your own blood, which is processed to concentrate platelets and growth factors. These are then injected into the skin to stimulate healing and reduce pigmentation. When combined with microneedling, PRP can be a highly effective treatment for melasma.
Preventing Melasma from Returning:
While treatments can help reduce melasma, prevention is key to long-term results. Here are some steps you can take to avoid melasma flare-ups:
-
Sun Protection: Sun exposure is one of the leading causes of melasma, so wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 is essential. Reapply every 2 hours when outdoors, and wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses.
-
Avoid Hormonal Triggers: If hormonal changes contribute to your melasma, talk to your doctor about adjusting medications, switching to a non-hormonal form of birth control, or managing other hormonal treatments.
-
Gentle Skincare: Choose gentle, non-irritating skincare products to avoid further aggravating melasma. Avoid harsh exfoliants or chemicals that can make your skin more sensitive to the sun.
-
Consistent Treatment: Once melasma is treated, it’s essential to maintain a consistent skincare routine, including sun protection, topical treatments, and regular check-ups with your dermatologist.
When to Seek Professional Help:
If over-the-counter treatments and home remedies don’t improve your melasma, it may be time to consult a dermatologist. A professional can assess your skin type and recommend a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. They can also monitor your progress to ensure that your melasma is being effectively managed.
Conclusion:
Melasma can be a persistent condition, but with the right treatments and proper sun protection, it’s possible to significantly reduce its appearance. Safe and effective options, including topical treatments, chemical peels, laser therapies, and microneedling, can help you achieve clearer, more even-toned skin. Prevention is crucial to avoid flare-ups, so always protect your skin from the sun and maintain a consistent skincare routine. If you're unsure which treatment is best for you, consulting a dermatologist can provide expert guidance to help you tackle melasma effectively.
For more information visit Dynamic Clinic PK.
What's Your Reaction?