Treatment-Resistant Depression Market: Addressing the Unmet Medical Need
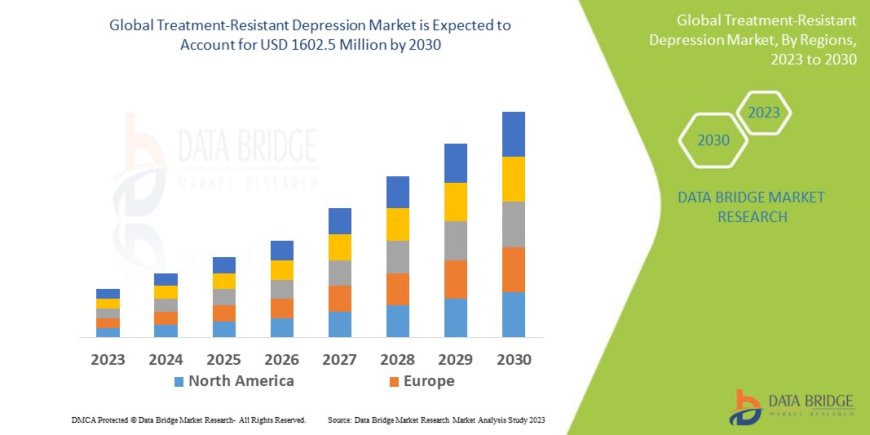
Data Bridge Market Research analyses a growth rate in treatment-resistant depression market in the forecast period 2023-2030. The expected CAGR of treatment-resistant depression market tend to be around 3.90% in the mentioned forecast period. The market was valued at USD 1180 million in 2022, and it would grow upto USD 1602.5 million by 2030
Introduction
Treatment-resistant depression represents one of the most challenging mental health conditions affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Defined as major depressive disorder that fails to respond adequately to at least two different antidepressant medications of adequate dose and duration, treatment-resistant depression affects approximately 30-50% of patients with depression. This condition significantly impacts quality of life, increases healthcare costs, and poses substantial challenges for patients, families, and healthcare systems globally.
The treatment-resistant depression market encompasses a diverse range of therapeutic approaches including novel pharmacological agents, medical devices, psychotherapy interventions, and emerging treatment modalities. Traditional treatment approaches such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants often prove insufficient for patients with treatment-resistant depression, necessitating the development of innovative therapeutic solutions. The market includes established treatments like electroconvulsive therapy and transcranial magnetic stimulation, alongside emerging therapies such as ketamine-based treatments, psychedelic compounds, and advanced neurostimulation devices.
The global treatment-resistant depression market has experienced significant growth driven by increasing awareness of mental health issues, improved diagnostic capabilities, and the development of innovative treatment approaches. Healthcare systems worldwide are recognizing the substantial burden of treatment-resistant depression and investing in research and development of effective therapeutic solutions. The market expansion is further supported by regulatory approvals of novel treatments, increased healthcare spending on mental health, and growing acceptance of alternative treatment modalities.
The Evolution of Treatment-Resistant Depression Understanding
The recognition and understanding of treatment-resistant depression have evolved significantly over the past several decades. In the early era of psychiatric medicine, depression was often viewed as a single condition with limited treatment options. The development of the first antidepressants in the 1950s marked a revolutionary advancement in depression treatment, but it soon became apparent that not all patients responded adequately to these medications.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the introduction of tricyclic antidepressants and later selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, which provided new hope for depression treatment. However, clinical experience revealed that a significant proportion of patients continued to experience persistent symptoms despite adequate treatment trials. This observation led to the formal recognition of treatment-resistant depression as a distinct clinical entity requiring specialized treatment approaches.
The 1990s marked a turning point in treatment-resistant depression research with the development of standardized criteria for defining treatment resistance. The introduction of rating scales and assessment tools enabled more precise measurement of treatment response and identification of patients who might benefit from alternative therapeutic approaches. This period also saw increased research into the biological mechanisms underlying treatment resistance, leading to better understanding of the neurobiological factors contributing to this condition.
The early 2000s witnessed significant advances in neurostimulation therapies for treatment-resistant depression. Electroconvulsive therapy, while effective, was associated with cognitive side effects and social stigma. The development of transcranial magnetic stimulation provided a less invasive alternative with fewer side effects. Deep brain stimulation emerged as an experimental treatment for severe cases, offering hope for patients with the most refractory forms of depression.
The 2010s brought breakthrough developments in ketamine-based treatments for treatment-resistant depression. The discovery that ketamine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, could produce rapid antidepressant effects in treatment-resistant patients revolutionized the field. This finding led to extensive research into glutamate-based treatments and the development of esketamine nasal spray, which received regulatory approval for treatment-resistant depression.
The current decade has seen renewed interest in psychedelic therapies for treatment-resistant depression. Clinical trials investigating psilocybin, MDMA, and other psychedelic compounds have shown promising results in treating resistant depression. These developments represent a paradigm shift in psychiatric treatment, moving beyond traditional monoamine-based approaches to explore novel mechanisms of action.
Market Trends Shaping Treatment-Resistant Depression Therapy
The treatment-resistant depression market is experiencing several transformative trends that are reshaping therapeutic approaches and creating new opportunities for patient care. One of the most significant trends is the increasing adoption of personalized medicine approaches in depression treatment. Advances in pharmacogenomics and biomarker research are enabling healthcare providers to identify patients who are more likely to respond to specific treatments, potentially reducing the trial-and-error approach that characterizes current depression treatment.
The integration of digital health technologies represents another major trend in treatment-resistant depression management. Digital therapeutics, smartphone applications, and wearable devices are being developed to monitor patient symptoms, track treatment response, and provide real-time interventions. These technologies offer the potential to improve treatment adherence, detect early signs of relapse, and provide continuous support for patients with treatment-resistant depression.
The growing acceptance of psychedelic therapies is creating new opportunities in the treatment-resistant depression market. Recent clinical trials have demonstrated the potential of psychedelic compounds such as psilocybin and MDMA in treating resistant depression. Regulatory agencies are increasingly open to approving these treatments, and investment in psychedelic research is growing substantially. This trend represents a fundamental shift in psychiatric treatment paradigms and opens new avenues for addressing treatment-resistant depression.
The development of novel neurostimulation techniques is advancing the field of device-based treatments for treatment-resistant depression. Innovations in transcranial direct current stimulation, focused ultrasound, and other non-invasive brain stimulation methods are providing new options for patients who do not respond to traditional treatments. These technologies offer the potential for more precise targeting of brain circuits involved in depression while minimizing side effects.
The increasing focus on combination therapies represents another important trend in treatment-resistant depression treatment. Researchers are exploring the potential of combining different treatment modalities such as medications, psychotherapy, and neurostimulation to achieve better outcomes. This approach recognizes that treatment-resistant depression may require multiple therapeutic interventions to address the complex underlying pathophysiology.
The growing emphasis on real-world evidence and patient-reported outcomes is influencing treatment development and evaluation in treatment-resistant depression. Healthcare systems are increasingly interested in treatments that demonstrate effectiveness in real-world settings and improve patient quality of life. This trend is driving the development of more patient-centered treatment approaches and outcome measures.
Challenges in the Treatment-Resistant Depression Market
The treatment-resistant depression market faces numerous significant challenges that complicate treatment development, delivery, and patient access. One of the primary challenges is the heterogeneity of treatment-resistant depression itself. The condition encompasses a diverse group of patients with varying symptom profiles, underlying causes, and treatment histories. This heterogeneity makes it difficult to develop universal treatment approaches and complicates clinical trial design and interpretation.
The lack of standardized diagnostic criteria for treatment-resistant depression presents ongoing challenges for researchers and clinicians. Different studies and clinical practice guidelines use varying definitions of treatment resistance, making it difficult to compare research findings and develop consistent treatment protocols. This lack of standardization can lead to delays in appropriate treatment initiation and difficulty in measuring treatment outcomes across different healthcare settings.
The high cost of many treatment-resistant depression therapies poses significant barriers to patient access. Novel treatments such as ketamine infusions, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, and deep brain stimulation can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance plans. The cost burden extends beyond direct treatment expenses to include indirect costs such as lost productivity, caregiver burden, and healthcare system utilization.
The complexity of treatment-resistant depression management requires specialized expertise and resources that may not be readily available in all healthcare settings. Many effective treatments require specialized equipment, trained personnel, and comprehensive monitoring protocols. The limited availability of specialized treatment centers and qualified providers can create access barriers for patients, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
Regulatory challenges present obstacles to bringing new treatments to market for treatment-resistant depression. The complexity of psychiatric conditions and the subjective nature of many outcome measures can complicate regulatory approval processes. The need for long-term safety and efficacy data can extend development timelines and increase costs for pharmaceutical and device manufacturers.
The stigma associated with mental health conditions continues to impact treatment-resistant depression care. Patients may delay seeking treatment or discontinue therapy due to social stigma, leading to poorer outcomes and increased healthcare costs. The stigma can also affect healthcare provider attitudes and treatment recommendations, potentially limiting access to effective interventions.
The limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms of treatment resistance presents challenges for developing targeted therapies. While research has identified several factors that may contribute to treatment resistance, the complex interplay between genetic, environmental, and clinical factors makes it difficult to predict which patients will develop treatment-resistant depression and which treatments will be most effective.
Market Scope and Therapeutic Landscape
The treatment-resistant depression market encompasses a comprehensive range of therapeutic interventions spanning pharmacological treatments, medical devices, psychotherapy approaches, and emerging treatment modalities. The pharmacological segment includes both established and novel antidepressant medications, with particular focus on drugs targeting alternative neurotransmitter systems beyond traditional serotonin-based approaches.
Ketamine-based treatments represent a significant segment of the pharmacological market, with both intravenous ketamine and FDA-approved esketamine nasal spray providing new options for treatment-resistant depression. These treatments work through NMDA receptor antagonism, offering a novel mechanism of action that can produce rapid antidepressant effects. The ketamine market segment is experiencing substantial growth as more healthcare providers adopt these treatments and insurance coverage expands.
The medical device segment includes various neurostimulation therapies such as electroconvulsive therapy, transcranial magnetic stimulation, vagus nerve stimulation, and deep brain stimulation. These devices offer non-pharmacological alternatives for patients who do not respond to medications or experience intolerable side effects. The device market is driven by technological advances that improve treatment precision, reduce side effects, and enhance patient comfort.
Psychotherapy interventions form another important component of the treatment-resistant depression market. Specialized therapy approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, and interpersonal therapy are often combined with pharmacological treatments to address the complex psychological and social factors contributing to treatment resistance. The integration of digital therapeutics and teletherapy platforms is expanding access to these interventions.
The emerging therapeutics segment includes psychedelic compounds, novel neurostimulation techniques, and innovative combination therapies. Psilocybin, MDMA, and other psychedelic substances are showing promise in clinical trials for treatment-resistant depression. These compounds work through different mechanisms than traditional antidepressants and may offer benefits for patients who have not responded to conventional treatments.
The market also includes supportive care services such as intensive outpatient programs, residential treatment facilities, and peer support programs. These services provide comprehensive care for patients with treatment-resistant depression, addressing not only the symptoms but also the functional impairments and social challenges associated with the condition.
The diagnostic and monitoring segment encompasses assessment tools, biomarker tests, and digital health technologies used to evaluate treatment response and guide therapeutic decisions. These tools are becoming increasingly important as the field moves toward personalized medicine approaches for treatment-resistant depression.
Market Size and Growth Analysis
The global treatment-resistant depression market has demonstrated robust growth over recent years and is projected to continue expanding significantly. The market was valued at approximately $1.8 billion in 2020 and is estimated to have reached $2.5 billion by 2025, representing a compound annual growth rate of approximately 8-10%. Market projections indicate continued strong growth, with the market potentially reaching $4.5-5.0 billion by 2030.
The pharmacological treatments segment currently represents the largest market share, accounting for approximately 60-65% of total market value. This segment is driven by the adoption of ketamine-based treatments, novel antidepressants, and combination therapies. The ketamine market alone is projected to reach $1.5-2.0 billion by 2030, reflecting the growing acceptance and utilization of these treatments.
The medical device segment accounts for approximately 25-30% of the market, with transcranial magnetic stimulation devices representing the largest component. The device market is experiencing steady growth driven by technological improvements, expanded clinical applications, and increasing adoption by healthcare providers. Deep brain stimulation and other advanced neurostimulation devices represent smaller but rapidly growing market segments.
The psychotherapy and supportive care services segment represents approximately 10-15% of the market, with growth driven by increased recognition of the importance of comprehensive care approaches. The integration of digital therapeutics and teletherapy platforms is expanding this segment and improving access to specialized care.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the dominant market, accounting for approximately 45-50% of global market value. This dominance is attributed to advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare spending, regulatory support for innovative treatments, and greater acceptance of mental health care. The United States represents the largest single market, driven by the availability of specialized treatment centers and insurance coverage for many treatment-resistant depression therapies.
Europe represents approximately 30-35% of the global market, with strong growth driven by increasing awareness of mental health issues, healthcare system support for innovative treatments, and regulatory approval of novel therapies. Countries such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and France are leading markets in the region.
The Asia-Pacific region accounts for approximately 15-20% of the global market but is experiencing the fastest growth rate. Increasing healthcare spending, growing awareness of mental health issues, and expanding healthcare infrastructure are driving market growth in countries such as Japan, China, and South Korea. The region presents significant opportunities for market expansion as healthcare systems continue to develop and mental health awareness increases.
Factors Driving Growth in Treatment-Resistant Depression Market
Multiple interconnected factors are driving sustained growth in the treatment-resistant depression market, creating opportunities for healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and medical device manufacturers. The increasing prevalence of depression worldwide represents a fundamental driver of market growth. The World Health Organization estimates that depression affects over 280 million people globally, with treatment-resistant depression affecting approximately 30-50% of these patients. This large patient population creates substantial demand for effective treatment options.
The growing awareness and acceptance of mental health issues is reducing stigma and encouraging more patients to seek treatment. Public awareness campaigns, celebrity endorsements, and media coverage have contributed to increased recognition of depression as a legitimate medical condition requiring professional treatment. This cultural shift is driving more patients to seek help and continue treatment despite initial treatment failures.
The economic burden of untreated depression is driving healthcare systems and employers to invest in effective treatment options. Treatment-resistant depression is associated with significantly higher healthcare costs, reduced productivity, and increased disability claims. The recognition that effective treatment can reduce these costs is motivating investment in innovative therapeutic approaches and expanded access to specialized care.
Regulatory support for innovative treatments is facilitating market growth through expedited approval processes and expanded treatment indications. The FDA's breakthrough therapy designation and other regulatory pathways have accelerated the development and approval of novel treatments for treatment-resistant depression. Regulatory agencies are increasingly recognizing the unmet medical need and providing support for innovative therapeutic approaches.
Advances in neuroscience research are providing new insights into the mechanisms underlying treatment-resistant depression and identifying novel therapeutic targets. The development of neuroimaging techniques, genetic analysis, and biomarker research is enabling more precise understanding of depression pathophysiology and treatment response. These advances are driving the development of more targeted and effective treatments.
The increasing availability of specialized treatment centers and qualified providers is improving access to care for patients with treatment-resistant depression. Healthcare systems are investing in mental health infrastructure, training programs for healthcare providers, and specialized treatment facilities. This expansion of treatment capacity is enabling more patients to receive appropriate care and driving market growth.
Investment in research and development is accelerating innovation in treatment-resistant depression therapies. Pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, and research institutions are investing heavily in developing new treatments and improving existing therapies. This investment is driving the pipeline of new treatments and creating opportunities for market expansion.
The integration of digital health technologies is expanding treatment options and improving patient outcomes. Digital therapeutics, smartphone applications, and wearable devices are providing new tools for monitoring symptoms, delivering interventions, and supporting patients with treatment-resistant depression. These technologies are making treatment more accessible and effective, driving market growth.
The growing acceptance of alternative and complementary therapies is expanding the treatment landscape for treatment-resistant depression. Treatments such as ketamine therapy, transcranial magnetic stimulation, and psychedelic-assisted therapy are gaining acceptance among healthcare providers and patients. This acceptance is driving adoption of these treatments and creating new market opportunities.
Insurance coverage expansion for mental health treatments is improving access to care and driving market growth. Mental health parity laws, increased insurance coverage for innovative treatments, and recognition of the cost-effectiveness of mental health care are reducing financial barriers to treatment. This expansion of coverage is enabling more patients to access effective treatments for treatment-resistant depression.
The development of personalized medicine approaches is improving treatment outcomes and driving market growth. Advances in pharmacogenomics, biomarker research, and artificial intelligence are enabling more precise treatment selection and dosing. These personalized approaches are improving treatment response rates and reducing the time to effective treatment, driving demand for specialized diagnostic and treatment services.
The increasing focus on patient-centered care is driving the development of more comprehensive and holistic treatment approaches. Healthcare providers are recognizing that effective treatment of treatment-resistant depression requires addressing not only symptoms but also functional impairments, social factors, and quality of life issues. This holistic approach is driving demand for comprehensive care services and integrated treatment programs.
The growing recognition of the importance of early intervention and prevention is driving investment in screening, assessment, and early treatment programs. Healthcare systems are implementing programs to identify patients at risk of developing treatment-resistant depression and provide early intervention to prevent progression to more severe forms of the condition. This focus on prevention is creating new market opportunities and driving demand for assessment and intervention services.
Other Trending Reports
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-pyrolysis-oil-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-cocoa-beans-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-gin-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-laser-plastic-welding-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-mobile-application-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-neurosurgery-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-non-alcoholic-beers-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/asia-pacific-ophthalmology-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/europe-ophthalmology-market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-ammonia-market
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0






























