What Are the Most Common Lung Diseases, and How Can You Prevent and Manage Them Effectively?
Common lung diseases include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer. Asthma is a chronic condition causing inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath.
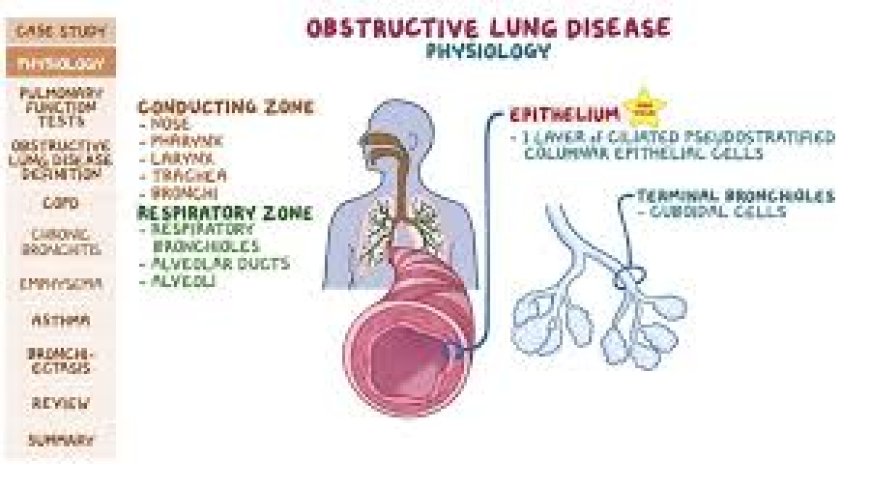
Introduction
Lung diseases are among the most prevalent health conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. They range from mild respiratory infections to chronic conditions like asthma and life-threatening illnesses such as lung cancer. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies for Lung Diseases is crucial for maintaining respiratory health and improving quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the most common lung diseases, their risk factors, and actionable steps to prevent and manage them effectively.
1. What Are Lung Diseases?
Lung diseases are disorders that affect the lungs and other parts of the respiratory system, impairing their ability to function properly. These conditions can interfere with breathing, oxygen exchange, and overall respiratory health. Lung diseases are broadly categorized into three types:
-
Airway Diseases: These affect the tubes (airways) that carry oxygen and other gases in and out of the lungs. Examples include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchiectasis.
-
Lung Tissue Diseases: These damage the structure of the lung tissue, making it difficult for the lungs to expand fully. Examples include pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis.
-
Lung Circulation Diseases: These affect the blood vessels in the lungs, leading to issues with oxygen exchange. Examples include pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary embolism.
2. Most Common Lung Diseases
A. Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that causes wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. It often starts in childhood and can be triggered by allergens, pollution, or exercise.
-
Symptoms: Wheezing, coughing (especially at night), difficulty breathing.
-
Prevention: Avoid triggers, use prescribed inhalers, and maintain a clean environment.
-
Management: Regular use of controller medications and quick-relief inhalers during attacks.
B. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a progressive lung disease that makes it hard to breathe. It includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, often caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke.
-
Symptoms: Chronic cough, mucus production, shortness of breath, fatigue.
-
Prevention: Quit smoking, avoid air pollutants, and get regular check-ups.
-
Management: Pulmonary rehabilitation, bronchodilators, and oxygen therapy.
C. Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. It occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the lungs, often due to smoking or exposure to carcinogens.
-
Symptoms: Persistent cough, chest pain, weight loss, coughing up blood.
-
Prevention: Avoid smoking, limit exposure to radon and asbestos, and adopt a healthy lifestyle.
-
Management: Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted drug therapies.
D. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, causing them to fill with fluid or pus. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
-
Symptoms: Fever, chills, cough with phlegm, difficulty breathing.
-
Prevention: Get vaccinated (e.g., pneumococcal and flu vaccines), and practice good hygiene.
-
Management: Antibiotics (for bacterial pneumonia), rest, and hydration.
E. Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition where lung tissue becomes scarred and stiff, making it difficult for the lungs to expand and contract properly.
-
Symptoms: Shortness of breath, dry cough, fatigue.
-
Prevention: Avoid exposure to environmental toxins and quit smoking.
-
Management: Medications, oxygen therapy, and lung transplantation in severe cases.
F. Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs but can spread to other organs. It is highly contagious and spreads through the air.
-
Symptoms: Persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss.
-
Prevention: Get vaccinated (BCG vaccine), and avoid close contact with infected individuals.
-
Management: Long-term antibiotic treatment.
G. Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow. It is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
-
Symptoms: Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heart rate.
-
Prevention: Stay active, manage weight, and use blood thinners if prescribed.
-
Management: Anticoagulant medications and clot-dissolving drugs.
3. Causes and Risk Factors of Lung Diseases
Several factors contribute to the development of lung diseases, including:
-
Smoking: The leading cause of lung cancer and COPD.
-
Environmental Pollutants: Exposure to air pollution, asbestos, and radon.
-
Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can lead to pneumonia or TB.
-
Genetics: Family history of lung diseases like asthma or pulmonary fibrosis.
-
Occupational Hazards: Jobs involving exposure to dust, chemicals, or fumes.
-
Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity.
4. Symptoms of Lung Diseases
While symptoms vary depending on the specific condition, common signs of lung diseases include:
-
Persistent cough
-
Shortness of breath
-
Wheezing
-
Chest pain or tightness
-
Fatigue
-
Coughing up blood
-
Frequent respiratory infections
If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
5. Diagnosis of Lung Diseases
Doctors use various tests to diagnose lung diseases, including:
-
Chest X-rays: To visualize the lungs and detect abnormalities.
-
CT Scans: For detailed images of the lungs.
-
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): To measure lung capacity and airflow.
-
Blood Tests: To check for infections or oxygen levels.
-
Bronchoscopy: To examine the airways using a thin, flexible tube.
-
Biopsy: To collect tissue samples for analysis.
6. Prevention of Lung Diseases
Preventing lung diseases involves adopting healthy habits and minimizing exposure to risk factors:
-
Quit Smoking: The single most effective way to reduce the risk of lung diseases.
-
Avoid Pollutants: Stay indoors on high-pollution days and use air purifiers.
-
Exercise Regularly: Improves lung capacity and overall health.
-
Get Vaccinated: Protect against flu, pneumonia, and TB.
-
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants.
-
Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands frequently to prevent infections.
7. Management and Treatment of Lung Diseases
Effective management of lung diseases requires a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle changes:
-
Medications: Bronchodilators, steroids, antibiotics, and antifungals.
-
Oxygen Therapy: For patients with low oxygen levels.
-
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A program of exercise, education, and support.
-
Surgery: To remove tumors or damaged lung tissue.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Quit smoking, exercise, and eat a balanced diet.
-
Regular Monitoring: Follow-up appointments to track progress.
8. Living with Lung Diseases
Living with a lung disease can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can improve your quality of life:
-
Stay Informed: Learn about your condition and treatment options.
-
Join Support Groups: Connect with others facing similar challenges.
-
Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
-
Stay Active: Engage in light exercises to strengthen your lungs.
-
Follow Your Treatment Plan: Take medications as prescribed and attend all medical appointments.
9. The Future of Lung Disease Treatment
Advancements in medical research are paving the way for innovative treatments for lung diseases:
-
Gene Therapy: Targeting genetic causes of lung diseases.
-
Stem Cell Therapy: Repairing damaged lung tissue.
-
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments based on individual genetic profiles.
-
Wearable Technology: Monitoring lung function in real-time.
10. Conclusion
Lung diseases are a significant global health concern, but with proper knowledge and proactive measures, many of these conditions can be prevented or managed effectively. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of your respiratory health and lead a fulfilling life. Remember, early detection and intervention are key to improving outcomes, so don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you experience any concerning symptoms.
What's Your Reaction?
















